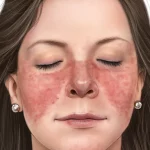
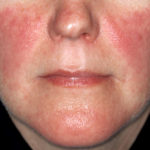
What is Lupus?
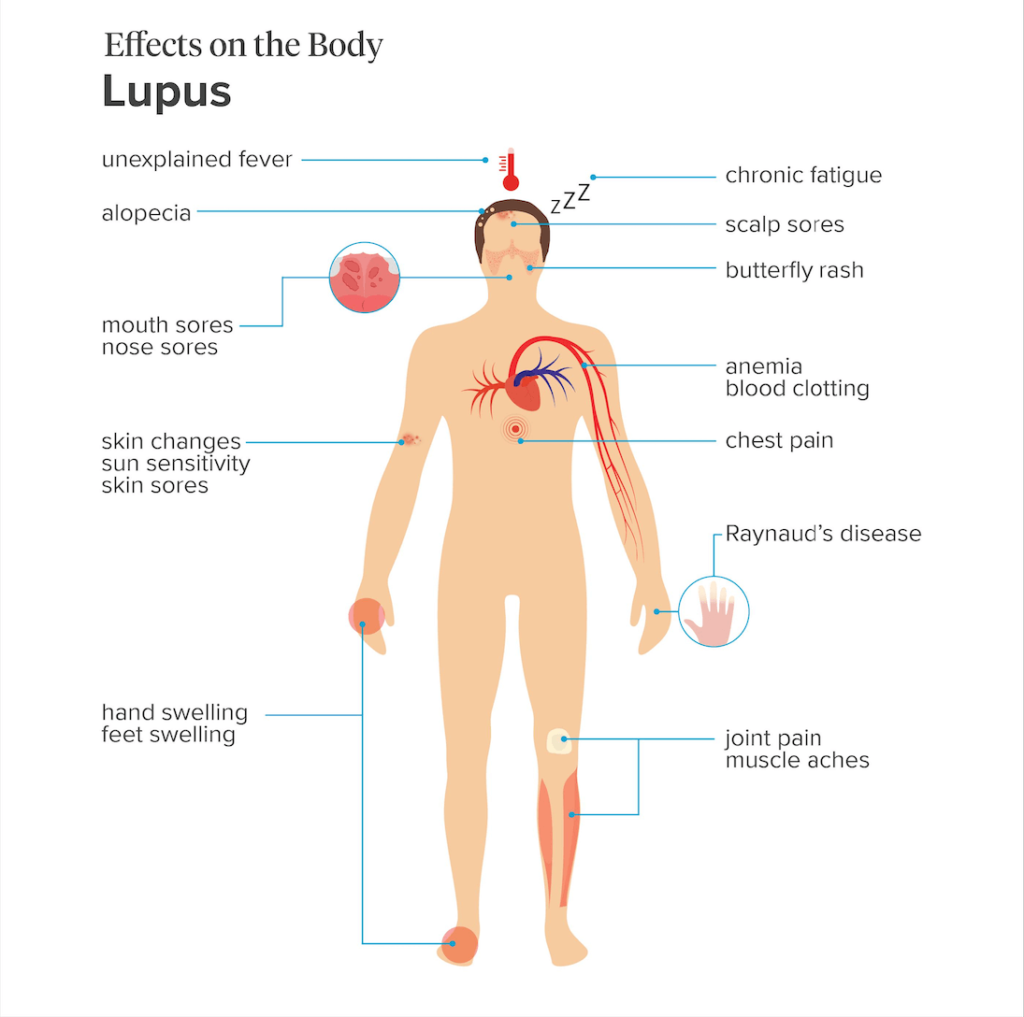
Lupus is an autoimmune chronic disease that causes your immune system to attack your body. Lupus symptoms affects about millions of Americans per year. Lupus causes inflammation and damage to the skin, joints, heart, lungs and kidneys.
Although the disease can be present at any age, it most commonly affects women in their 40s and 50s.
Why Lupus is Called Lupus?
Lupus is in Latin and means wolf. The word wolf is associated with misfortune – the same as being cursed. That’s why in old times, being cursed and having a bad luck was called lupus.
Lupus Symptoms in Women
Lupus Symptoms Checklist
Lupus affects both sexes. However, the symptoms in women may be different from those in men. Women are more likely to develop lupus than men because women have less Testosterone to offset the effects of estrogen.
While there are many different types of lupus, the most common lupus symptoms checklist include fever and inflammation in multiple joints (particularly the knees, hips, ankles and wrists).
In addition to these symptoms, some women with lupus will have skin rashes and joint pain.
Additional most common symptoms of lupus in women (lupus side effects) are:
- Fatigue
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Headaches
These symptoms can vary from one woman to the next but are all very similar to other chronic diseases such as fibromyalgia or chronic fatigue syndrome.
Women who suspect they may have something wrong with them should visit their doctor for an evaluation. Keep in mind that symptoms of lupus are varied and often difficult for doctors to diagnose.
Lupus Pictures Symptoms
Here are some sample lupus pictures symptoms of women around face and hand area:
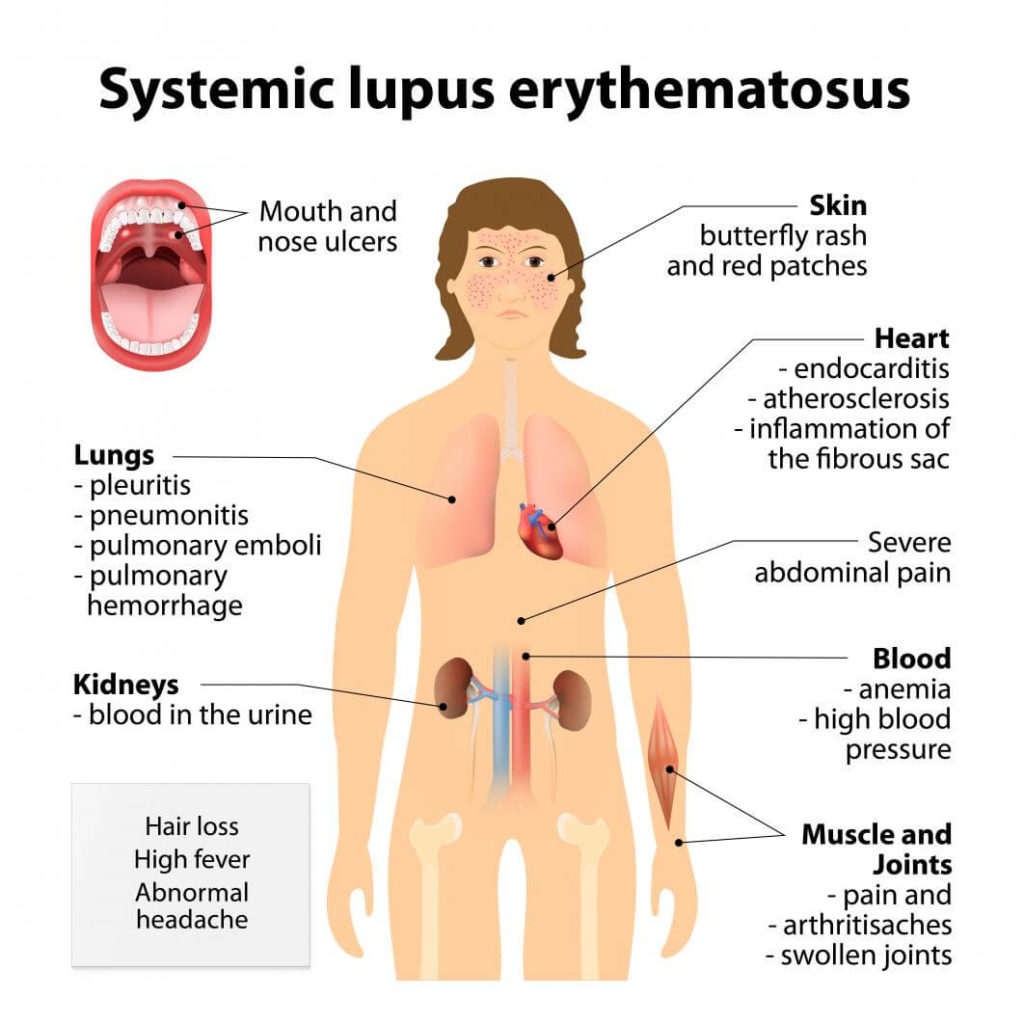
Lupus Causes
One of the more common causes of lupus symptoms in women is polycystic ovary syndrome. Other causes of lupus symptoms in women include autoimmune diseases, systemic lupus erythematosus, and Sjogren’s syndrome.
Lupus Diagnosis
As with any health problem, it is important to find out as much about the situation as possible before going for a diagnosis. It is not always easy for a Lupus diagnose in women because there are many symptoms that overlap with common ones like arthritis, fibromyalgia, and other conditions!
Lupus is diagnosed by a series of tests that can confirm the diagnosis, such as:
1. Lupus Skin Biopsies Test
Lupus is diagnosed by a dermatologist who does skin biopsies to check for the presence of antinuclear antibodies (ANA). ANAs are proteins produced in the body that are associated with autoimmune disorders. The immunoglobulin tests can be used in addition to these involved procedures.
2. Lupus Blood Test
When your blood is checked, any positive antibodies will be tested against typical and atypical antigens (parts of some diseases). If you have positive tests for both atypical and typical antigens, this is a definite confirmation that you have lupus.
If there are no signs or symptoms of lupus, your doctor might test you for auto-immune diseases like certain types of rheumatism in order to rule out lupus.

Lupus Types
There are three types of lupus and symptoms vary depending on which type a patient has to go through:
1. Systemic Lupus
Systemic Lupus affects different organs in the body and causes symptoms like fatigue and weight gain.
2. Discoid Lupus
Discoid Lupus creates areas or patches of redness on the skin that can cause itchiness and inflammation in those areas.
3. Panniculitis Lupus
Panniculitis Lupus is most common in the abdomen, chest, back, or neck causing pain and discomfort in these areas.
Lupus Treatment
It’s sad to know that there is no known cure yet for lupus, but treatments may reduce its severity.
While medications aren’t typically recommended as a first-line treatment they can be helpful in managing certain symptoms.
Treatment can be medical or physical; a variety of pharmaceuticals and other medicines are used to reduce symptoms, improve overall quality of life, and prevent future complications.
The treatment may include immunosuppressants such as Corticosteroids, Cytotoxics, or Antimalarial drugs.
Immunosuppressants suppress the immune system, which helps prevent inflammation and autoimmunity from progressing.
Cytotoxic drugs directly attack the cells of the body’s immune system that are causing fibrosis and tissue damage in the organs.
Antimalarial drugs reduce symptoms by reducing swelling in joints and soft tissue, which means it can also be used for folic acid deficiency.
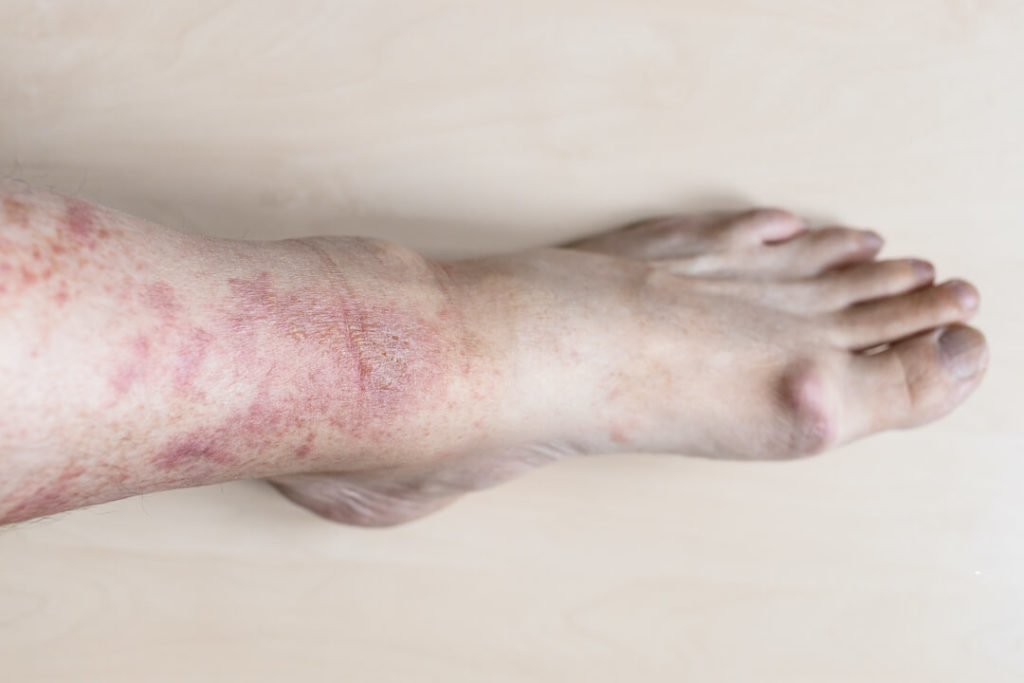
Are Lupus Rashes Itchy?
Yes. Lupus rashes are itchy. The rash can appear anywhere on the body, but most commonly appears on the face, hands, feet and arms. The rash is red and scaly, and will flake too. Lupus rashes occur most often in the summer months, but can also be present year-round.
Lupus Rash Treatment
Where do lupus rashes appear?
The lupus rash is a telltale sign of lupus, which can look like a tan or cream-colored patch on the skin or lupus circular rash on face.
This patch often has different shapes on it and may have some scabbing. The cause for this rash is unknown at this time, but it does not appear to be responsive to sunlight or the sun’s rays.
One of the most common treatments for lupus rash is to use a topical cream containing cortisone. This can help reduce symptoms, but it doesn’t address the underlying cause of lupus rashes.
How Often Does Lupus Flare Up?
Lupus can flare up at any time, and not just when you are in the sun or stressed. So the short answer is: It flares up whenever your body decides.
Lupus flareups can be triggered by infections, stress, hormonal changes, and physical trauma. Generally these flares are brief and resolve quickly without any long-term consequences.
Lupus with Negative Ana
Lupus with negative ana is a rare form of lupus. This form is characterized by an increased risk of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, lupus nephritis or mixed connective tissue diseases.
Furthermore, patients with this form of lupus are more likely to develop severe side effects caused by the medication that controls their disease; in particular the drug prednisolone (the steroid treatment for the disease).
Most patients have symptoms corresponding to those seen in people without an increased risk of autoimmune diseases, but some patients develop severe complications such as damage to the heart valves and arteries.
Lupus with negative ana also increases your risk of developing a number of other chronic diseases including cardiovascular disease and cancer.
Lupus Mouth Sores
Lupus mouth sores are caused by white blood cells called lymphocytes. The lymphocytes can build up in the mouth and cause inflammation, which leads to the sores. Lupus mouth sores typically appear on the tongue or the edges of the lips, but they can be found anywhere on the body.
In some cases, these sores will clear up without treatment, but if a person’s symptoms persist for more than three months, she may need treatment from a doctor.
Lupus Symptoms Hands
The lupus symptoms hands can be very similar to other diseases and health conditions. The hands are one of the most commonly affected areas, although any organ in the body can be affected. How do you know if your hands are part of your Lupus symptoms? Here are some things to consider:
- What else seems to bother your hands?
- Do they hurt in the morning or get worse with stress or fatigue?
- Is there swelling and/or redness or skin discoloration on your hands that does not go away on its own?
- Are there rashes or skin lesions on your hands that itch, burn, sting, feel numb or tingle?
- Do you have temperature sensitivity in your hands?
If you experience any of the above lupus symptoms hands then you should see a doctor.
Lupus on Scalp
Lupus on scalp is often due to a condition called alopecia areata. This is an autoimmune disease where the body mistakenly targets its own hair follicles causing them to fall out.
One of the common treatments for alopecia areata is steroid injections into the bald areas, so your doctor may be thinking that you have lupus on scalp if he/she sees redness or swelling at the site of these injections.
More extensive biopsies can then be performed to determine the cause of your lupus on scalp symptoms, and treatment adjusted accordingly.
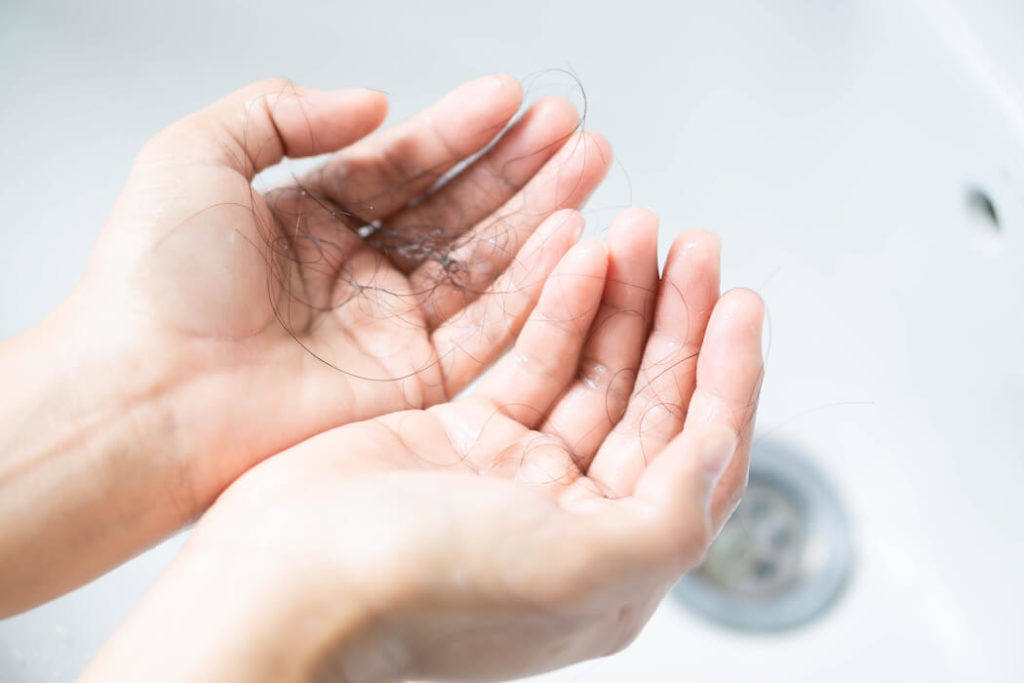
Lupus and Hair Loss
Can lupus cause hair loss?
Yes. Hair loss is one of the most common lupus symptoms for women. A woman with lupus may experience significant thinning or complete baldness in some parts of her scalp. The cause of this hair loss may be internal bleeding from an autoimmune disorder like lupus, chemotherapy, genetics or other causes.
There is some evidence that shows that minoxidil and oral finasteride treatments can promote regrowth of hair follicles with lupus-related hair loss. Seek your doctor’s advice on the course of treatment available for the hair loss.

Lupus Diet
A diet that is rich in fruits and vegetables can help keep your lupus symptoms under control. It is important to avoid sugar, sugar-containing products and processed foods high in sodium, like deli meats such as bologna and salami.
A diet low in carbohydrates and rich in protein and fat can help prevent chronic inflammation caused by lupus.
Is Lupus Contagious?
No. Lupus is not contagious. You can’t catch it from a person and there is no proof of that. However, sometimes the disease is triggered by an environmental reason. If a parent has lupus, there is a chance that their baby can inherit the disease from them.
Is Lupus Deadly?
Yes. Lupus can kill you as it’s a fatal illness, but it’s not that easy to die from lupus! Lupus is a very manageable disease if you can get proper treatment and avoid complications.
Lupus with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Lupus versus rheumatoid arthritis: Lupus is an autoimmune diseases that attacks the body, while rheumatoid arthritis is a condition that involves inflammation of the joints. Patients with lupus are often designated as having rheumatoid arthritis. Lupus with rheumatoid arthritis are most common in women.
Lupus Life Expectancy
Lupus life expectancy has improved greatly over the years and is now equivalent to that of a person without lupus.
Patients who were diagnosed with this illness and followed up with their doctors regularly, have enjoyed almost the same life span of normal people.
Final Thoughts
Lupus is a chronic illness that affects women disproportionately. One in every two hundred women will develop lupus during their lifetime, but the symptoms are not always clear and can be indistinguishable from other diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and fibromyalgia.
Keep in mind that most people who suffer from this disease also experience one or more autoimmune disorders, which means they’re at risk of developing other health complications such as diabetes, heart disease and lung failure.
There are several symptoms of lupus, an autoimmune disorder that can affect women in different ways. The most common lupus side effects include unexplained fevers, severe fatigue, and joint pain. Always consult your doctor if you have these or other unusual symptoms.
While there is no treatment for lupus, fortunately, the Lupus Foundation of America has a whole network of affiliates and doctors who specialize in lupus.
If you enjoyed reading this article, you may want to checkout Humira Injection Pen – Humira Medicine Uses and Side Effects.
Useful resources about lupus: